What is Satellite Observation?
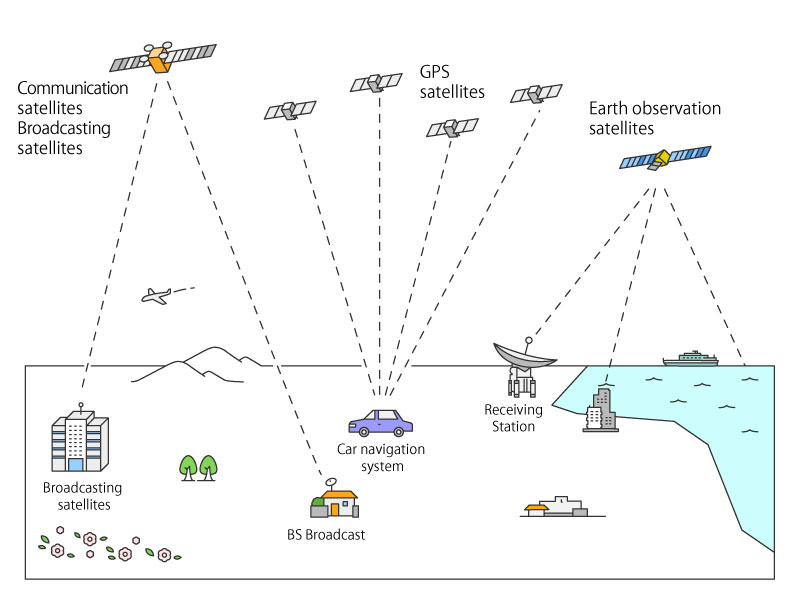
What kinds of satellites are operated?
Earth-orbiting satellites are divided into three categories in accord ance with their missions.
- Transferring information : Communication technology…Communication satellites, Broadcasting satellites
- Defining positions : Navigation technology…Global positioning satellites
- Measuring objects : Remote sensing technology…Earth observation satellites
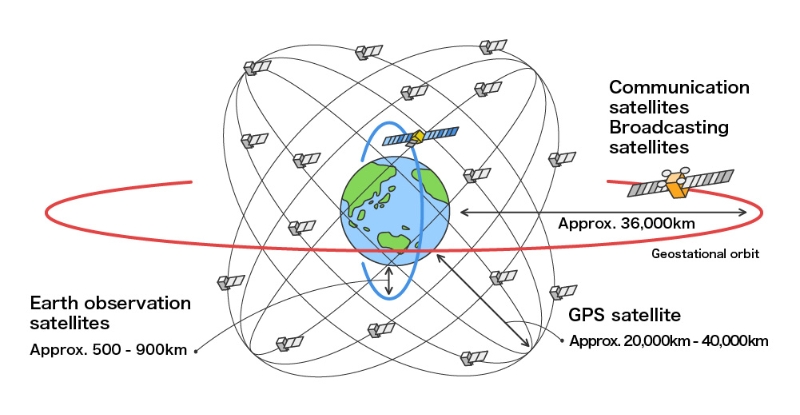
What kinds of orbits are assigned?
- Geostationary orbit…The satellite on this orbit takes a position around the equator and moves at the same speed of the Earth’s rotation
- Sun-synchronous quasi-periodical orbit…This orbit is made by combining the synchronous orbit and quasi periodical orbit
- Orbits other than 1 & 2…Non-synchronous orbit
1.Geostationary orbit
The geostationary orbit is used for communication, broadcasting and weather satellites. This orbit takes a position around the equator at a distance of 36000km from the Earth’s surface. Because the satellite moves at the same speed as the Earth’s rotation, the satellite maintains the same position over a certain point of the Earth’s surface. This orbit is useful for “serving at all times in a certain area” such as communication, broadcasting, weather forecasting missions. But these satellites can not be used on the opposite side area of the Earth.
“Himawari” (Japanese weather forecasting satellite) is assign ed to this orbit.
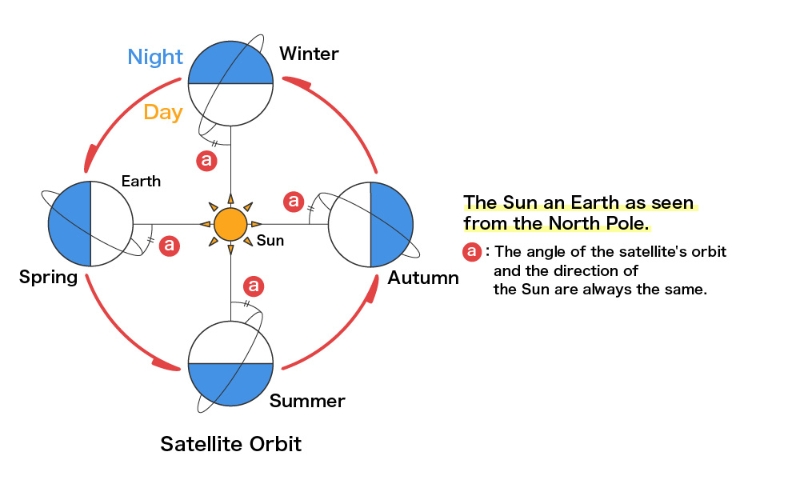
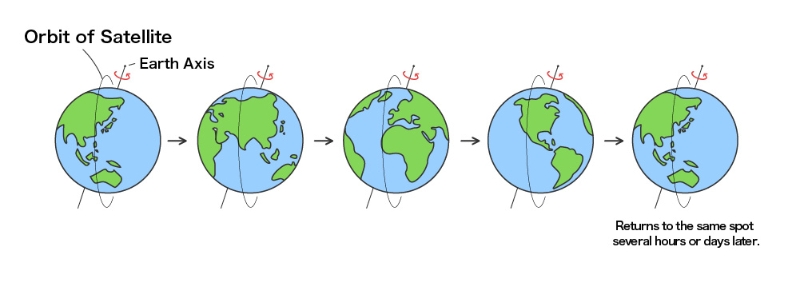
2.Sun-synchronous quasi-periodical orbit
This orbit is made by combining the synchronous orbit and the quasi periodical orbit, and many Earth observation satellites employ this orbit. The satellite on this orbit passes by a certain place of the Earth’s surface at the same local solar time (the orbit plane keeps a constant solar angle), so the satellite observes the same sun light reflection from the Earth’s surface. This enables the observed images of each place to be easily compared and analyzed with the same sun light reflection phenomena. The satellite on this orbit observes all Earth surfaces , so they are utilized in all areas of the world. Also, the satellite on this orbit has a regression cycle in which the satellite passes the same place after respective pass cycles.
Then this satellite observes the certain place with the same local solar time and same orbit position for each respective pass cycles. “DAICHI” (Japanese Advance d Earth Observing Satellite) and the “LANDSAT” series use this orbit.
3.Other orbits
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite is assign ed to an orbit that observes all tropical regions along the equator at various local solar times.
The orbit is selected for the purpose of its mission.
What is Satellite Remote Sensing?
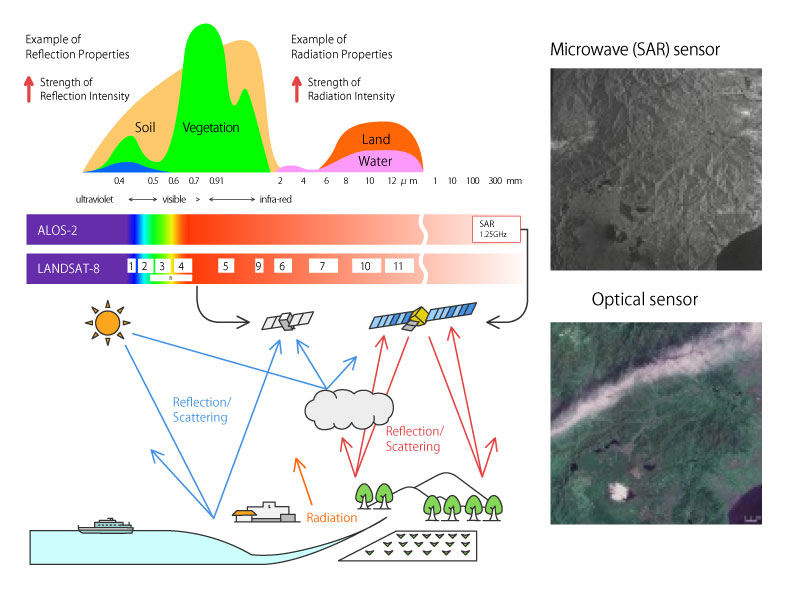
Earth observation satellites are the satellites equipped with remote sensing technology. Various sensors are equipped on these satellites in accordance with their respective missions.
Typical sensors
The sensors are categorized into three kinds.
1. Observing the reflection of sunlight or the Earth’s radiation : Optical sensors
These sensors observe the reflection of sunlight including invisible ultraviolet and near, medium, thermal infrared rays, and the Earth’s radiation.
2. Transmitting microwaves to the target and receiving the reflected microwave from the target : Active microwave sensors
These sensors transmit microwaves to the target and receive the reflected microwaves from the target. This method is not affected by clouds and does not require the sunlight, so it can be used in all weather conditions and during the night . Typical sensors under this category are the Synthetic Aperture Radars (SAR) and Precipitation Radars (PR).
3. Observing the reflected microwave from the target : Passive microwave sensors
These sensors observe the proper microwaves reflected from the target. It can be used in all weather conditions and during the night.
What can be observed
Optical sensors
Vegetative conditions, ground surface temperatures, sea surface temperatures, ground elevation, cloud conditions, water distribution
Active microwave sensorss
Vegetative conditions, ground elevation, cloud conditions, water distribution
Passive microwave sensorss
Ground surface temperatures, sea surface temperatures, cloud conditions